Hello. I’ve been talked into writing another blog post about my latest puzzle to appear in the Puzzlebomb. Spelling Bees appeared in the May and June issues. The solver is presented with a honeycomb grid containing letters and one bee (of the insect variety; the grid may contain several or no Bs). Their task is to find the two words (or phrases) that can be  traced along a path through every cell (to use jargon that will be familiar to cruciverbalists and beekeepers alike) in the honeycomb grid. The bee acts as a wild card and will stand for a different letter in both words. The cells which are the first and last letters of each word are shaded to give an extra helping hand.
traced along a path through every cell (to use jargon that will be familiar to cruciverbalists and beekeepers alike) in the honeycomb grid. The bee acts as a wild card and will stand for a different letter in both words. The cells which are the first and last letters of each word are shaded to give an extra helping hand.
Development of the puzzle
As much as I love cryptic crosswords (for the record: significantly more than is healthy) and pure logic puzzles, I also have a soft spot for word games and puzzles where words are treated merely as a set of objects to be toyed with, their meanings and usage irrelevant. There are already plenty of these of course: Scrabble, codewords, Countdown and the find-as-many-words-using-these-letters-always-including-the-central-letter game that appears in every newspaper under a different name. I wanted to try my hand at making one of this sort of puzzle.
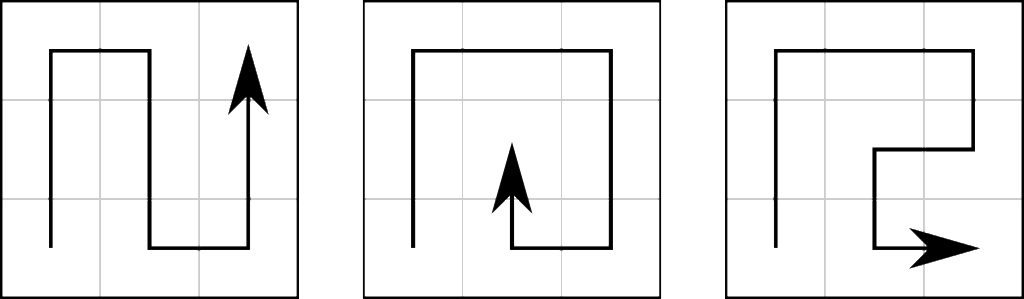
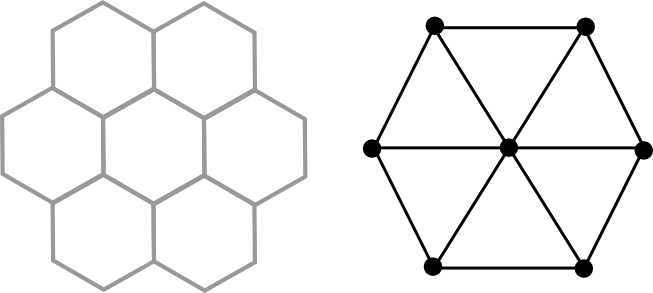
There’s a puzzle in the Manchester Evening News in which you have to find a 15-letter word or phrase in a pyramid-shaped ‘maze’, and probably inspired by this I thought about having a 3×3 grid in which two different words, anagrams of each other, can be found. There were two problems with this: firstly, there aren’t actually that many nine-letter-word anagram pairs – CARTHORSE and ORCHESTRA is probably the most well-known and pleasing one, but they’re not so easy to come by; and secondly, there are only a few different paths through a 3×3 grid (an N-shape, a spiral, a sort of-R shape and rotations and reflections of these; see above). So the hexagon-based grid format came in, with each cell having up to six neighbours instead of four, and the wild card was added to allow not-quite-exact anagrams to be used. I reckoned this would allow enough flexibility for a good number of decently fun puzzles to be makeable, though I wouldn’t know for certain until I started trying to make them. And of course, from the hexagons came the idea of the bee to represent the wild card and from there came the name.
Construction of the puzzles
As you’ll have probably guessed, particularly if you read the blog for my last puzzle, the brunt of the legwork involved I outsource to the computer. The overall process goes something like this:
Human
- Choose the grid pattern for the puzzle, and tell it to Computer. Computer stores it as a sequence of neighbour-sets, so for this example it would store the grid as $((1,2,3),(0,3,4),(0,3,5),(0,1,2,4,5,6),(1,3,6),(2,3,6),(3,4,5))$, with the
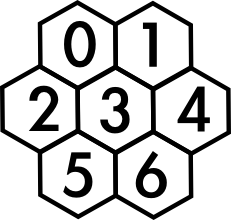 $n$th member of the sequence giving the neighbours of the cell numbered $n$. (To be awkward, Computer likes to call what we call the $1$st member the ‘$0$th’ member, so $(1,2,3)$ is the $0$th member of the list and is the set of neighbours of cell $0$.)
$n$th member of the sequence giving the neighbours of the cell numbered $n$. (To be awkward, Computer likes to call what we call the $1$st member the ‘$0$th’ member, so $(1,2,3)$ is the $0$th member of the list and is the set of neighbours of cell $0$.)
Computer
- Find every path through every cell of the grid. Computer does this with a simple backtrack search: it builds up a path by repeatedly adding to the end of the path the lowest-numbered cell that is adjacent to the cell currently at the end, and hasn’t already been visited. When Computer successfully finishes a path it writes it down, and when it finishes a path or gets stuck in a dead end, it tries to replace the last cell in the path with a larger numbered cell, and if it can’t, gets rid of it and tries again with the new last cell. So in our example Computer would first build up the path $0 \to 1 \to 3 \to 2 \to 5 \to 6 \to 4$ , and write it down. Obviously the $4$ can’t be replaced with a higher cell (there are no cells left unused) so it’s got rid of. The $6$ can’t be replaced by anything bigger so it goes too. Nor can the $5$ (since $5$ isn’t next to $6$, the only number bigger than it). The ‘stump’ path $0 \to 1 \to 3 \to 2 \to$ is now left, and Computer sees that it can replace the $2$ with a $5$, giving $0 \to 1 \to 3 \to 5 \to$. It adds the $2$ on (being the lowest-numbered neighbour of $5$ not already in the path). But now it’s at a dead end: $2$ has no neighbours not already in the path. So the $2$ goes, and the $5$ is replaced with the $6$…. This goes on for a bit, until eventually Computer has found all the paths. It knows this has happened because the path dies back all the way to nothing ($0 \to 3 \to 6 \to$ goes to $0 \to 3 \to$ goes to $0 \to$ goes to oblivion).
- Computer trawls its word-list (the same one as used for Hilbert’s space-filling crossword) for a pair of words that differ in only one letter (and the order the letters are in of course). Clearly, this is the kind of task Computer loves, and so I shall omit a description of the boring details of this aspect. Once Computer has found a pair, it writes them down with an asterisk in place of the letter that will become the bee in each word.
- Having found a suitable pair, Computer checks them against the grid patterns to see if they fit. Computer effectively writes the first word in the grid along one of the paths, and then checks every other path to see if it spells out the second word. If it doesn’t, Computer moves the first word to a different path and tries again.
- Computer repeats the find-words-check-words process until it finds a pair that fit in the grid. Computer shows Human the puzzle and goes and has a lie down.
Human
- Human checks that both the words in the puzzle are reasonably common words that a solver will have a fighting chance of getting, and that the words are not too similar that the puzzle is trivial (you might be disappointed to find that the solution to this puzzle is SAFFRON and AFFRONT). Human (probably with help from Computer) should probably also check that there aren’t any other words that can be found in the grid, leading to multiple correct solutions, but to be honest Human is a little lax about this.
A little bit of Maths
Since this neither a puzzles site nor a computer programming site but a maths site, here are some maths-y questions that I have considered while making these puzzles/writing this blogpost.
1. How many paths through a grid are there?
Well, firstly let’s stop this talk of ‘grids’ and ‘cells’ and put this in proper maths terms. The puzzle grid can be considered as a graph $\mathcal G$, with the cells as the vertices and two cells joined by an edge if and only if they’re adjacent. We want to know the number of paths of length $|\mathcal G|$. I would be surprised to learn that there was a significantly easier way to find this number than searching for them all as described above. For small graphs you can do it by hand: for our example from above, the three fundamentally different paths are shown here, and counting them all rotated and reflected and backwards we get a grand total of $84$. For the ten-vertex graph used for most of the Puzzlebomb puzzles, Computer reports a total of $656$ different paths.
2. How likely is it that a given pair of anagrams fits into the grid?
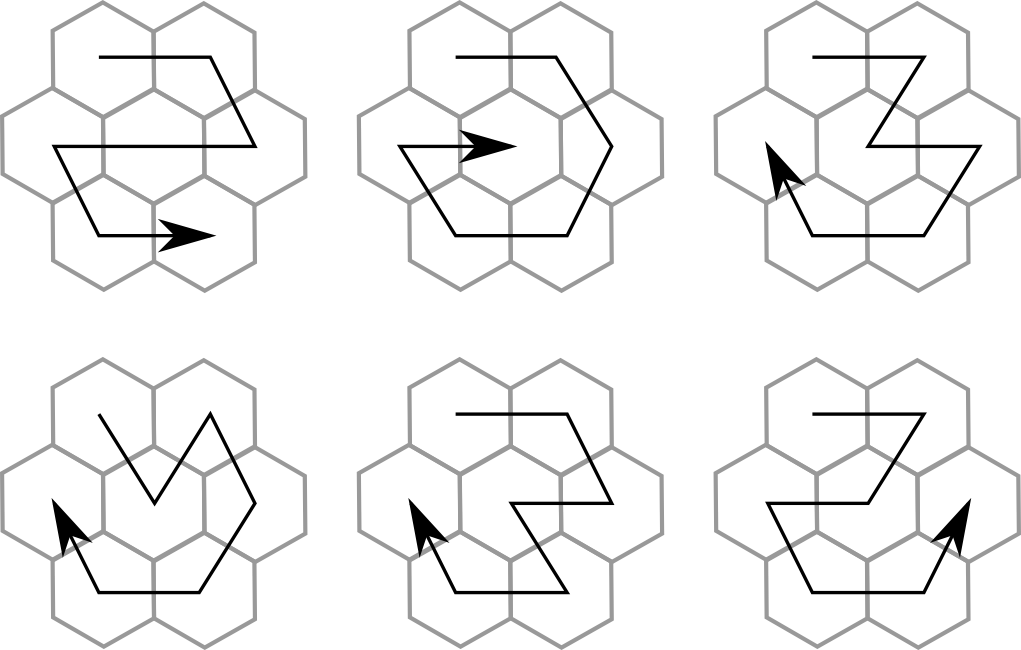 On the face of it, $780$ different paths perhaps doesn’t seem like all that many, especially when we consider the anagrams. What determines whether a pair of words fit into the grid is precisely how they are anagrams: what permutation of the letters transforms one word into the other. You might know that the number of permutations on ten letters is $10!=3,628,800$: rather more than $780$. But of course both words in the puzzle are assigned a path, and this pair of paths gives a second permutation of ten objects that we need to correspond to the first (see the diagram below for an explanation of how this works). $780$ paths gives $303,810$ possible pairs of paths, a decent fraction of the total number of ways the words could be jumbled.
On the face of it, $780$ different paths perhaps doesn’t seem like all that many, especially when we consider the anagrams. What determines whether a pair of words fit into the grid is precisely how they are anagrams: what permutation of the letters transforms one word into the other. You might know that the number of permutations on ten letters is $10!=3,628,800$: rather more than $780$. But of course both words in the puzzle are assigned a path, and this pair of paths gives a second permutation of ten objects that we need to correspond to the first (see the diagram below for an explanation of how this works). $780$ paths gives $303,810$ possible pairs of paths, a decent fraction of the total number of ways the words could be jumbled.

Two different paths through the grid generate a particular anagram permutation: in this case, the first letter moves to second position; the second letter to seventh position; the seventh letter to the first position; and the other four stay still. A mathematician might write this down as $(1,2,7)$.
However, some of these pairs of paths will give rise to the same permutation. The graph is the same turned upside-down or reflected left-right or top-bottom, so any pair of paths that differs from another only by one of these symmetries will give the same permutation: if you turn a Spelling Bees puzzle upside down then it’s still the same puzzle. Formally, if a pair of paths is the image of another pair under an automorphism of the graph then both pairs will give rise to the same permutation
Bonus Question 1: is the converse statement true: are two path-pairs giving the same permutation necessarily related by a graph automorphism?
So we have a set of permutations available to us as potential anagrams, which we might call the set of permutations realizable as Spelling Bees on that graph. Given a set of permutations, a natural question to ask is whether it forms a group. Now, in the above I glossed over some details that are important if we want to talk about groups: I gave the number of pairs of paths simply as $780\choose2$. But of course we could take both paths to be the same, giving the identity permutation (important if you want a group; not so good for making fun puzzles). And the order you consider the paths in makes a difference here: the same paths in the other order give the inverse permutation (again important for getting a group but not so much for a puzzle since it corresponds to thinking about the two words in the other order, which is still the same puzzle). I think it’s clear after a bit of consideration that if there’s only one fundamental type of path, such as in a $2\times2$ square grid, where there is only a c-shaped path and its rotations and reflections, then we do get a group, since all the paths are related by graph automorphisms, so every pair of paths just gives you the permutation of the automorphism that connects them. So for a $2\times2$ square, we get the $8$ permutations that form the symmetry group of a square, $D_8$. (Some people call this group $D_4$, giving the number of sides of the associated polygon rather than the number of elements of the group. These people are wrong to do this but let’s not get into that right now.)
Bonus Question 2: are there graphs whose set of permutations-realizable-as-Spelling-Bees form a group, other than the ones described above? (I do not know the answer to Bonus Question 2 and have made no great attempt to check that it is not boring or near-impossible or both. Have fun!)
Anyway, let us move away from group theory. Dependent on the answer to BQ1, we have perhaps around $100,000$ different permutations available to us, suggesting that a pair of words has about a 3% chance of fitting into the grid somehow. (Incidentally, seeing all the pairs of lovely almost-anagram words that flash by on the computer screen but must be rejected because they don’t fit in the grid is a very sad process. Who wouldn’t want to see a puzzle with the answers AUTOMOBILE and OUT ON A LIMB? Sadly it is not to be.) In fact, Computer finds fits for more like 15% of the pairs it tries. This is doubtless due to the fact that among actual dictionary words, anagrams are most likely to arise where words have long strings of letters in common (these are precisely the puzzles that Human gets rid of), and that these permutations are more likely to be realizable as puzzles, given the restrictions placed on the graphs by the hexagon structure of the grids. For example, I just set Computer going and in 4 tries it alighted on the very similar pair WAPENSHAWS and WEAPONSHAW (your guess is as good as mine), then took about 40 tries to find the pleasing but altogether too bear-heavy WHITE BEARS and BEAR WITH ME; 3 tries to find DESOLATING and DESALTINGS, with their DES and TING overlaps; 8 to get BULL-HEADED and BULLETHEAD and finally 33 tries to get to one that might be suitable for an actual puzzle (please, don’t spoil the answer in the comments):