Earlier this week I posted a matrix multiplication worksheet on Mastodon.
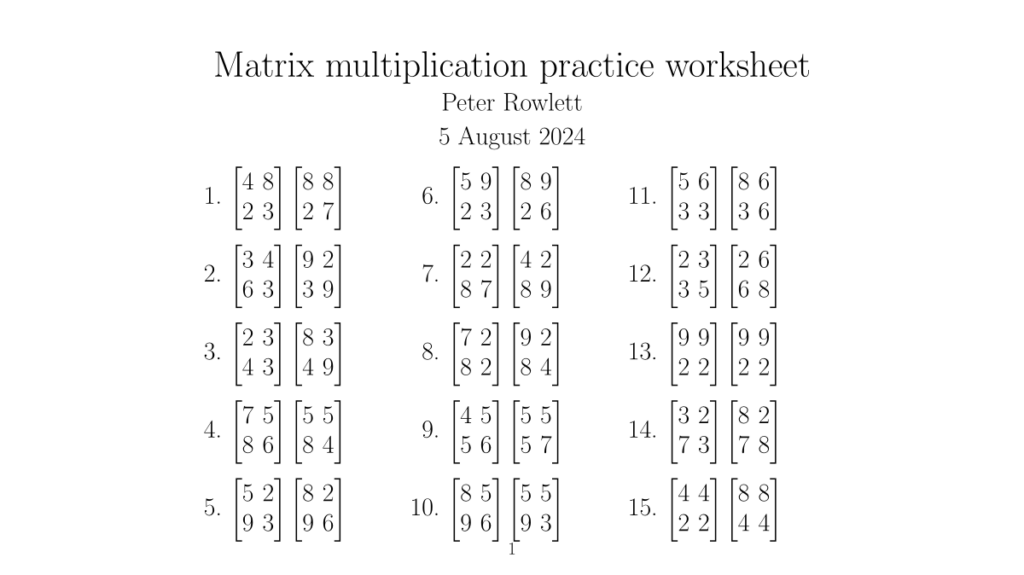
If you do some of these, you might spot what’s funny about them. For example.
\[ \Large \begin{bmatrix}
\color{navy}{4} & \color{navy}{8}\\
\color{navy}{2} & \color{navy}{3}
\end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix}
\underline{\color{blue}{8}} & \underline{\color{blue}{8}}\\
\underline{\color{blue}{2}} & \underline{\color{blue}{7}}
\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}
\color{navy}{4}\underline{\color{blue}{8}} & \color{navy}{8}\underline{\color{blue}{8}}\\
\color{navy}{2}\underline{\color{blue}{2}} & \color{navy}{3}\underline{\color{blue}{7}}
\end{bmatrix} \]
That is, the answer to each question can be made by treating the element in the first matrix as the first digit and the corresponding element in the second matrix as the second digit in the answer element. This is not how matrix multiplication works, and ought to be funny if I hadn’t totally over-explained the joke!
I saw one of these in a meme that Katie posted in the Finite Group chat and it got me thinking about how these work.
If we set up the matrices like this
\[ \begin{bmatrix}
a & b\\
c & d
\end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix}
e & f\\
g & h
\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}
10a+e & 10b+f\\
10c+g & 10d+h
\end{bmatrix} \]
Then we establish four equations with eight unknowns.
\[ \begin{align*}
ae + bg &= 10a+e\\
af+bh &= 10b+f\\
ce+dg &= 10c+g\\
cf+dh &= 10d+h
\end{align*}\]
Since there are more unknowns than equations, these don’t have a single solution. What I wanted was to find integer solutions with all values single-digits. I wrote some Python code to find these. I removed some that look overly symmetrical – either the rows of the matrix are identical, or the same matrix is repeated. This left 73 items.
From these 73 items, I wrote a second Python script that picks 20 of them at random and builds these into a LaTeX worksheet. For the Mastodon post I reformatted this into the shape and size that I thought would display better on social media, and added in one of the squared matrices for an extra hint something weird is up, hoping people might notice this isn’t just a boring post about matrix multiplication practice!
You can view these scripts and associated files on GitHub.