Over at the Finite Group, members (including me and Katie) have been discussing what in maths news has excited us this year. Here’s a summary.
Brayden Casella and fellow authors claimed that there exists a non-terminating game of Beggar-My-Neighbour, solving one of John H. Conway’s anti-Hilbert problems. Beggar-My-Neighbour is a card game similar to War in which two players deal cards onto a shared pile, aiming to win all the cards into their hand. Matthew Scroggs made a bot: Beggar-my-neighbour forever. In other game theory news, Othello is solved.
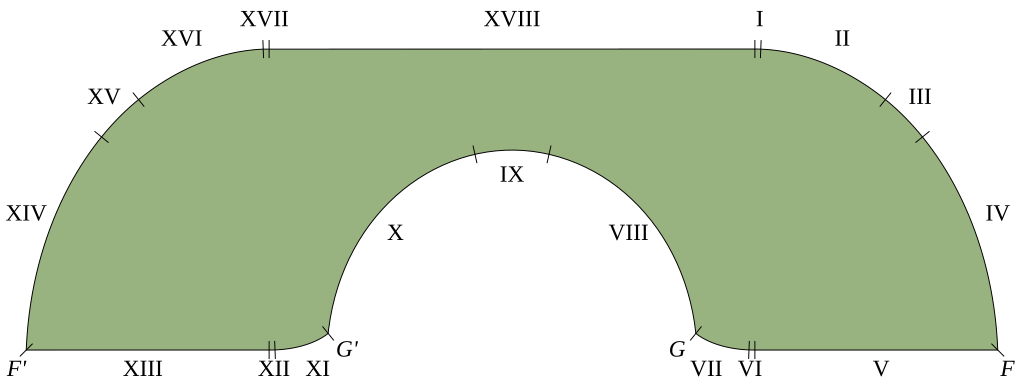
Jineon Baek claims a resolution to the moving sofa problem. This considers a 2D version of turning a sofa around an L-shaped corner, attempting to find a shape of largest area. (There are some nice animations at Wolfram MathWorld.) Baek offers a proof that the shape above, created by Joseph L. Gerver in 1992, is optimal.
The Great Internet Mersenne Prime Search (GIMPS) announced a new Mersenne prime: \(2^{136,279,841}-1\). You can get maximum excitement about this news from Ayliean on TikTok, and join in the fun by signing up to record yourself saying a chunk of the prime for the Say The Prime project.
One thing that’s new, apart from the prime itself, is that the work was done on a network of GPUs, ending “the 28-year reign of ordinary personal computers finding these huge prime numbers”. Also this was the first GIMPS prime discovered using a probable prime test, so the project chose to use the date the prime was verified by the Lucas-Lehmer primality test as the discovery date. In other computation news, the fifth Busy Beaver number has been found, as well as 202 trillion digits of pi.
A new elliptic curve was discovered, breaking a record set in 2006 and pushing at the limits of current methods for finding them. Here’s some background on the curves and some of the characters involved.
This year also saw a proof of the geometric Langlands conjecture, and this article explains why this is such a big deal.
We’re all still excited about the discovery of the aperiodic monotiles, and the result passed peer review and was published this year.
And finally, it may not be top research news, but 2024 was also the year that Colin Beveridge started his Double Maths First Thing newsletter. Subscribe to the newsletter here, and check out the archive of past issues here at The Aperiodical.
Finite Group is a friendly online mathematical discussion group which is free to join, and members can also pay to access monthly livestreams (next one Friday 20th December 2024 at 8pm GMT and recorded for viewing later). The content isn’t at the level of the research mathematics in this post, but we try to have a fun time chatting about interesting maths. Join us!